A Railway route was being laid by the British Government in parts of West Punjab and Sindh (present-day Pakistan) in India. They came across a mound amidst the plains near the village of Harappa. Digging through the plain, they discovered burnt bricks of the exact shape and size. So many of them, as though there underneath the mound lies a huge wall of some fort. The Railway work was stopped, and ASI took over. A few years before this, an Italian youth had discovered some weird-looking seals at a site at Kalibangan. Unfortunately, before he could report it to the ASI chief, he was taken ill and died. With this discovery, the Indian subcontinent that Britishers believed had flourished only a few years before Alexander (some put the date around 800B.C.) was forced to shift the date of the beginning of this civilisation by almost a million years.
The Vedas, Puranas, and local folktales were something the Indians were proud of; now, for the first time, they had proof of the actual historical evidence of the Vedic eras. Layers of civilisation were unearthed at many sites all over the Saptasindhu Valley. ( Indus, Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Saraswati, Yamuna and Ganga) Almost 2500 sites remain identified, and the rest are still buried under the land. The earliest cities were dated to around 5000 B.C., and thus it is believed that settlement, cultivation and village life started in India almost around 9000B.C., much before its contemporary civilisations in Egypt, Greece or Mesopotamia. India is thus the oldest of civilisations, and its cities are among the first in the world. Even at the lower levels of excavation, Hindu gods such as Shiva( In Linga form), Mother Goddess (of harvesting, similar to Annapurna avatar of Parvati), Indra, Agni and Saraswati are found. Hinduism is the oldest surviving religion in the world from then on. Altars meant for offering "yajna" to Agni are also found in the main cities of the valleys.
 |
| The Lower Town of Mohenjo-Daro |
Now, what makes the Indus Saraswati Civilisation a wonder?
Firstly, the civilisation was mainly dependent on the river Saraswati (which was considered Mythical for its mention in the Vedas and Epics of India), which was discovered as a dried-up basin near the Ghaggar River of today. Most sites were found on either bank of this dried-up basin. The drying up of the river for reasons still undiscovered was the chief reason behind the decline of this civilisation.
Strangely enough, till today, no foolproof translation of its script could be done, so their means of communication is still unknown to us. From that language developed the later Brahmi Language of the Vedic Era. The language was in some sort of signs and symbols that are found in many Harappan seals and amulets. Pictures of animals and deities are also found, making historians believe that they were god-fearing, nature-loving people. The toy carts, Chaturanga and dice games found in the ruins give a vivid idea of their lives. Cotton was extensively used in making clothes and food, including the cultivation of cereals and vegetables. Rice was considered a luxury to Harappans (commonly meaning people of this civilisation).
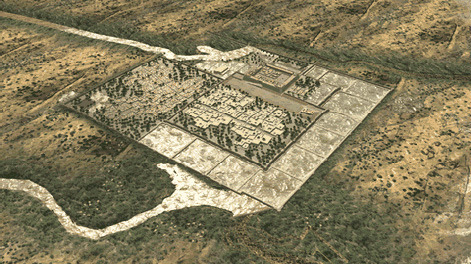 |
Artistic impression of Dhola Vira
|
There was no sign of wars or enemy attacks in this vast land. No weapons were found at the sites, and a few spears or sharp knives that were found were concluded to be used for household and religious activities. Castles and forts discovered are assumed to be more of a working place for the elites. Some even assume that much like today, Harappans had democratic or social republic states and not a monarchy. No signs of warfare way into the last phases around 900 B.C., stating that the native Indians had no conflict with the nomadic Aryans who came into India and settled here in groups over a large period. In fact, they lived in perfect harmony and picked up each other's talents. Aryans adapted to the native ways of lifestyle and religion, while the natives learned to use a few weapons and use and tame horses from the Aryans. Inter-tribe marriages or alliances were another sign of harmony in the civilisation. So the question remains that if not war, then what destroyed it? If they moved away from the Saraswati basin and further east, then where did they settle?
Some believe that the oldest cities of Hastinapur, Dwarka, Varanasi, and many sites down south are the answer. They moved further east and built cities and empires. After the end of this civilisation, the prominence of universities such as Taxila, Ujjaini and Nalanda grew, and Hinduism also developed out of its initial rituals to idol worship, extended marriage rituals, and even cremation of the dead, who were till then buried. Burial sites in the Saraswati Civilisation are found along with mass graves. The dumping of masses in open burials also provides a theory that there might have been a plague that hit the land and forced people to move away.
Some geologists suggest that a huge earthquake rippled through the Indo-Gangetic plain, changing the course of many rivers, even the Yamuna, which left flowing westward towards Saraswati and started flowing eastward into the Ganges. Thus, the Saraswati dried up soon after this, and the Ganges valley gained prominence as the biggest cities grew on its banks. The drying up of Saraswati was a huge blow, and the earthquake also caused extensive damage to the Harappan way of life. Historians used to believe that the Harappan civilisation extended only up to the present-day Rajasthan and Gujarat, but many sites have been found near Himachal Pradesh and also Uttarakhand in the eastern parts of the country. The next question lies in how the cities so far from one another used to stay connected. The River routes considered the easiest means of transport, too, were in fact very far from one another. Then what was the meaning of easy communication?
 |
| Toy Carts of Mohenjo-Daro |
The ancient texts give us a series of strange machinery and measurements that still remain a mystery. "Pushpak ", for example, is some kind of aeroplane described in the Ramayana and ancient Puranas. If something similar was used is unknown. Another mystery is whether these sites had independent rules and autonomous authority or whether the cities were all under the same administration. This cannot be known until the scripts are deciphered. The Mystery Man remains the figure commonly called the Priest-King. Whether he was some kind of great ruler or a significant legend is unknown.
Another mystery is the relationship of this civilisation with the world outside the Hindukush Range. The Egyptian and Mesopotamian scripts mention trade with the Indian subcontinent and names of Indian Gods, materials from the Harappan cities are found in Mesopotamia and even Greece, but strangely enough, nothing from these civilisations was found at the Saraswati Valley sites. In fact, there would have been no trace of sea routes if not for the huge port of Lothal that was discovered in Gujarat. Lothal provided important insight into the port system of the Harappans with its methods of warehousing, preservation, taxes and other details found at Lothal. The man-made port is indeed a wonder of civilisation.
A unique feature of this civilisation is that no big structures have been found at any sites that stood out as different, like the Egyptian Pyramids, Hanging Gardens of Babylon or even the temples of Greece. The towns have two and three-storey houses, attached bathrooms, drainage systems, garbage disposal systems, manholes, a Cemetery and a lot of common things found in cities of today. But all these at that time and era are unimaginable. So, in their uniqueness, the whole cities themselves of Mohenjo-Daro, Harappa, Lothal and the Fortified town of Dholavira are wonders. The cities are so vast that they could not have been fully excavated till today. Mohenjo-Daro is estimated to be the largest city of contemporary times.
Further Reads: Early Indians, The Lost River Saraswati





